Technology
Humphrey Visual Field Analyzer
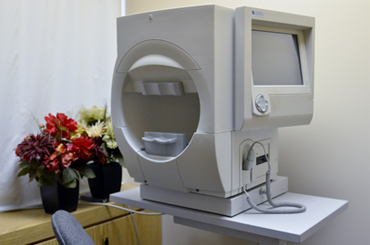
The Humphrey field analyzer is an instrument that checks the sensitivity of our peripheral and central vision. It involves focusing on a central fixation light while small lights flicker around it. The flickering lights will vary in intensity. During the test, a patient will need to push a button every time a light is detected. Each eye is usually tested separately.
A visual field test helps diagnose many serious eye and brain conditions. Examples include diseases of the eye nerve like glaucoma, tumors in the brain or around the eye nerve, multiple sclerosis, macular diseases, stroke (brain or eye nerve), medication induced toxicity of the macula.
This test also allows us to test peripheral vision for the Ministry Of Transportation.
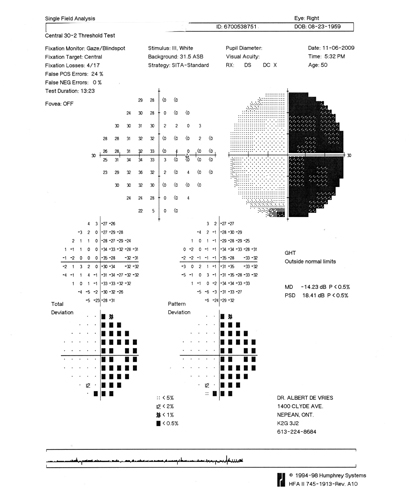
Example of a patient with a brain tumour:
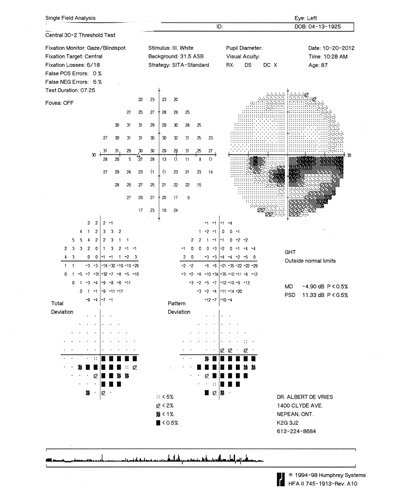
Example of a patient with glaucoma:
Non – Contact Tonometery
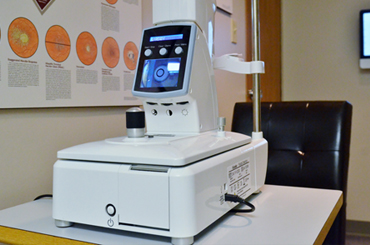
A gentle puff of air is used to measure intraocular pressure. If this measurement is abnormal, it may lead to permanent damage of the eye (optic) nerve, a painless/initially symptom free condition called glaucoma.
Pachmate
This hand held instrument uses ultrasound to measure the thickness of the cornea. This technique is called corneal pachymetry. A thin cornea indicates a greater risk for glaucoma. In fact, the Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study, the results of which were published in 2002, indicated that people with thinner central corneas are 3.5 times more likely to have permanent vision loss, resulting from glaucoma. Pachymetry can also be useful in diagnosing conditions like Fuch's dystrophy or chronic edema secondary to contact lens wear; disorders that will result in a thickened cornea.
Cannon Fundus camera
The retinal camera is used to take a digital snapshot of the inside of each eye. It allows us to examine the retina, macula and optic nerve better. It also helps us monitor your eye health more thoroughly over time. It is a straight forward procedure where the doctor focuses onto your retina without using radiation and without touching your eye. It is followed by a brief flash of light to take the image.
After taking the digital image, the doctor utilizes the computer software to analyze the image in more detail. This varies from zooming in to see more fine details, to filtering out certain wavelengths to focus on particular layers of the retina or measuring changes over time (like the size of a mole in the eye or shape of the eye nerve).
Miniscule changes in the eye could indicate serious eye disease. For example, in glaucoma the rim of the eye nerve slowly thins down over time; patients do not feel or notice this until the sight threatening disease has advanced more. Digital imaging can help us identify certain retinal changes earlier and initiate treatment/referral before your vision is jeopardized.
We believe it is an essential part of an eye exam. At present we recommend the following:
- Patients between the ages of 20-45 should have the test done every 2-3 years
- Patients between the ages of 45-65 should have the test done every 2 years
- Patients over the age of 65 should have the test done annually
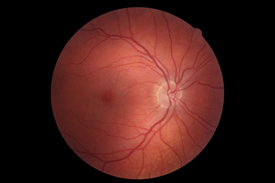 |
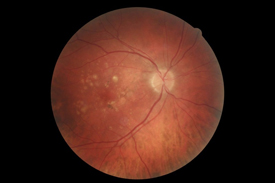 |
| Normal appearance of the back of the eye | Macular degeneration |
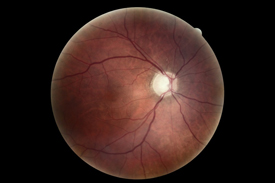 |
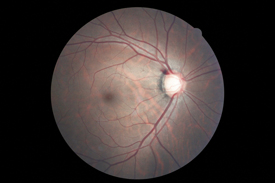 |
| Glaucoma | Glaucoma Drance Hemorrhage |
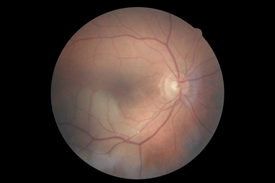 |
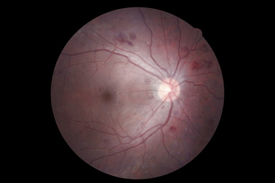 |
| Embolus in retinal arteriole | Diabetic retinopathy |
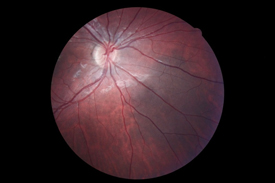 |
|
| Retinal nevus |

